Question 13
A Linux administrator needs to redirect all HTTP traffic temporarily to the new proxy server 192.0.2.25 on port 3128. Which of the following commands will accomplish this task?
Correct Answer:D
The command iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT -- to-destination 192.0.2.25:3128 adds a rule to the nat table that redirects all incoming TCP packets with destination port 80 (HTTP) to the proxy server 192.0.2.25 on port 3128. This is the correct way to achieve the task. The other options are incorrect because they either delete a rule (-D), use the wrong protocol (top instead of tcp), or use the wrong port (81 instead of 80). References: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 12: Managing Network Connections, page 381.
Question 14
A user is asking the systems administrator for assistance with writing a script to verify whether a file exists. Given the following:
Which of the following commands should replace the
Correct Answer:A
The command if [ -f "$filename" ]; then checks if the variable $filename refers to a regular file that exists. The -f option is used to test for files. If the condition is true, the commands after then are executed. This is the correct way to replace the <CONDITIONAL> string. The other options are incorrect because they either use the wrong option (-d tests for directories), the wrong syntax (missing a semicolon after the condition), or the wrong keyword (while is used for loops, not conditions). References: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 16: Writing and Executing Bash Shell Scripts, page 493.
Question 15
A junior administrator updated the PostgreSQL service unit file per the data-base administrator's recommendation. The service has been restarted, but changes have not been applied. Which of the following should the administrator run for the changes to take effect?
Correct Answer:B
To apply changes to a systemd service unit file, the administrator needs to reload the systemd daemon using the command systemct1 daemon-reload (B). This will make systemd aware of the new or changed unit files. The other commands will not reload the systemd daemon or apply the changes. References:
✑ [CompTIA Linux+ Study Guide], Chapter 7: Managing System Services, Section:
Modifying Systemd Services
✑ [How to Reload Systemd Services]
Question 16
Some servers in an organization have been compromised. Users are unable to access to the organization’s web page and other services. While reviewing the system log, a systems administrator notices messages from the kernel regarding firewall rules:
Which of the following commands will remediate and help resolve the issue?
Correct Answer:A
The command iptables -F will remediate and help resolve the issue. The issue is caused by the firewall rules that block the access to the organization’s web page and other services. The output of dmesg | grep firewall shows that the kernel has dropped packets from the source IP address 192.168.1.100 to the destination port 80, which is the default port for HTTP. The command iptables -F will flush all the firewall rules and allow the traffic to pass through. This command will resolve the issue and restore the access to the web page and other services. The other options are incorrect because they either do not affect the firewall rules (ip route flush or ip addr flush) or do not exist (iptables - R). References: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 18: Securing Linux Systems, page 543.
Question 17
A Linux administrator needs to resolve a service that has failed to start. The administrator runs the following command:
The following output is returned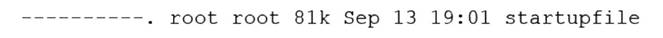
Which of the following is MOST likely the issue?
Correct Answer:A
The most likely issue is that the service does not have permissions to read or write the startupfile. The output of systemct1 status startup.service shows that the service has failed to start and the error message is “Permission denied”. The output of ls -l /etc/startupfile shows that the file has the permissions -rw-r--r--, which means that only the owner (root) can read and write the file, while the group (root) and others can only read the file. The service may not run as root and may need write access to the file. The administrator should change the permissions of the file by using the chmod command and grant write access to the group or others, or change the owner or group of the file by using the chown command and assign it to the user or group that runs the service. The other options are incorrect because they are not supported by the outputs. The file size, owner, and group are not the causes of the issue. References: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 11: Managing Files and Directories, pages 345-346.
Question 18
A Linux administrator provisioned a new web server with custom administrative permissions for certain users. The administrator receives a report that user1 is unable to restart the Apache web service on this server. The administrator reviews the following output:
[ root@server ] # id user1
UID=1011 (user1) gid=1011 (USER1) groups=1011 (user1), 101 (www-data), 1120 (webadmin)
[ root@server ] # cat /etc/sudoers.d/custom.conf
user1 ALL=/usr/sbin/systemctl start httpd, /usr/sbin/systemctl stop httpd webadmin ALL=NOPASSWD: /etc/init.d.httpd restart, /sbin/service httpd restart,
/usr/sbin/apache2ctl restart
#%wheel ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL
Which of the following would most likely resolve the issue while maintaining a least privilege security model?
Correct Answer:D
The custom.conf file grants sudo privileges to user1 and webadmin for managing the Apache web service, but it uses different commands for each of them. User1 is allowed to use systemctl to start and stop the httpd service, while webadmin is allowed to use init.d, service, or apache2ctl to restart the httpd service. However, the user1 is unable to restart the service, only start and stop it. To fix this, user1 should be able to use the same commands as webadmin, which can be achieved by listing webadmin as a group in the custom.conf file, using the syntax %groupname. This way, user1 will inherit the sudo privileges of the webadmin group, and be able to restart the Apache web service without compromising the least privilege security model.
References
✑ Sudo and Sudoers Configuration | Servers for Hackers, section “Groups”
✑ Chapter 12. Managing sudo access - Red Hat Customer Portal, section “12.1.
Configuring sudo access for users and groups”