Question 7
The applications team is reporting issues when trying to access the web service hosted in a Linux system. The Linux systems administrator is reviewing the following outputs:
Output 1:
* httpd.service = The Apache HTTPD Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled) Active: inactive (dead)
Docs: man:httpd(8) man:apachectl(8) Output 2:
16:51:16 up 28 min, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.07
Which of the following statements best describe the root cause? (Select two).
Correct Answer:CD
The httpd.service is the Apache HTTPD Server, which is a web service that runs on Linux systems. The output 1 shows that the httpd.service is inactive (dead), which means that it is not running. The output 1 also shows that the httpd.service is disabled, which means that it is not enabled to auto start at boot time. Therefore, the statements C and D best describe the root cause of the issue. The statements A, B, E, and F are incorrect because they do not match the output 1. References: [How to Manage Systemd Services on a Linux System]
Question 8
Using AD Query, the security gateway connections to the Active Directory Domain Controllers using what protocol?
Correct Answer:C
Using AD Query, the security gateway connects to the Active Directory Domain Controllers using Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). LDAP is a protocol that provides access to directory services over a network. AD Query uses LDAP queries to retrieve information about users and groups from Active Directory Domain Controllers without installing any software on them. AD Query does not use Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI), Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS), or Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) to connect to Active Directory Domain Controllers. References: Check Point Certified Security Administrator (CCSA) R80.x Study Guide, Chapter 5: User Management and Authentication, page 69.
Question 9
A systems administrator is investigating why one of the servers has stopped connecting to the internet.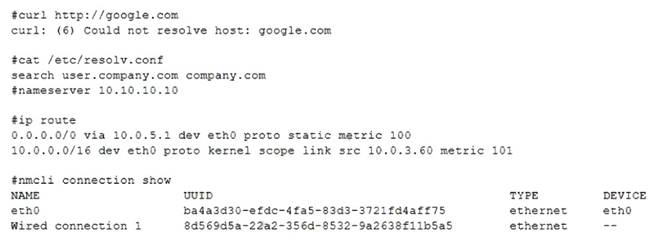
Which of the following is causing the issue?
Correct Answer:D
The issue is caused by the lack of a default route defined in the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3 file. A default route is a special route that specifies where to send packets that do not match any other routes in the routing table. Without a default route, the server will not be able to communicate with hosts outside its local network. The default route is usually configured with the GATEWAY option in the network interface configuration file. For example, to set the default gateway to 192.168.1.1, the file should contain:
GATEWAY=192.168.1.1
The other options are not causing the issue. The DNS address is not commented out in the configuration file, it is specified with the DNS1 option. The search entry in the /etc/resolv.conf file is correct, it specifies the domain name to append to unqualified hostnames. Wired connection 1 is online, as indicated by the ONBOOT=yes option and the output of ip link show enp0s3 command. References: Configuring IP Networking with nmcli; Configuring IP Networking with ifcfg Files
Question 10
An administrator accidentally installed the httpd RPM package along with several dependencies. Which of the following options is the best way for the administrator to revert the package
installation?
Correct Answer:D
The yum history undo last command will undo the last transaction, which in this case is the installation of the httpd RPM package and its dependencies. This will remove the packages that were installed and restore the previous state of the system. See How to undo or redo yum transactions and yum history.References1: https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/undo- redo-yum-transactions2: https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man8/yum.8.html#HISTORY
Question 11
A user reported issues when trying to log in to a Linux server. The following outputs were received:
Given the outputs above. which of the following is the reason the user is una-ble to log in to the server?
Correct Answer:D
The user1 password is expired. This can be inferred from the output of the chage -l user1 command, which shows the password expiration information for user1. The output shows that the password expired on 2020-10-01, and the account expired on 2020-10-08. This means that user1 cannot log in to the server unless the password and account are reactivated by the system administrator.
The other options are not correct based on the outputs above. User1 does not need to set a long password, because the output of the passwd -S user1 command shows that the password has a minimum length of 5 characters, which is met by user1’s password. User1 is not in the incorrect group, because the output of the groups user1 command shows that user1 belongs to the app group, which is presumably the correct group for accessing the server. The user1 shell assignment is not incorrect, because the output of the grep user1
/etc/passwd command shows that user1 has /bin/bash as the default shell, which is a valid and common shell for Linux users.
Question 12
To harden one of the servers, an administrator needs to remove the possibility of remote administrative login via the SSH service. Which of the following should the administrator do?
Correct Answer:B
The administrator should set PermitRootLogin to no in the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file to remove the possibility of remote administrative login via the SSH service. The PermitRootLogin directive controls whether the root user can log in using SSH. Setting it to no will deny any remote login attempts by the root user. This will harden the server and prevent unauthorized access. The administrator should also restart the sshd service after making the change. The other options are incorrect because they either do not affect the SSH service (/etc/hosts.deny or /etc/pam.d/sshd) or do not prevent remote administrative login (PubKeyAuthentication). References: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 13: Managing Network Services, page 413.