Question 55
You need to invert the color intensity of a quantitative range. Which option should you use?
Correct Answer:A
To invert the color intensity of a quantitative range in Tableau, you should use the "Reversed" option. This option inverts the color scheme so that the colors representing the higher values are swapped with those representing the lower values. For example, if a color scale initially shows dark colors for high values and light colors for low values, using "Reversed" will switch this so that dark colors represent low values and light colors represent high values. This option is particularly useful for better visual distinction and
interpretation in certain data scenarios.
Question 56
_______ are a local copy of a subset or entire data set that you can use to share data with others, when you need to work offline, and improve performance.
Correct Answer:D
According to the official Tableau documentation:
Depending on the version the extract was created in, Tableau extract files can have either the .hyper or .tde file extension. Extract files are a local copy of a subset or entire data set that you can use to share data with others, when you need to work offline, and improve performance. For more information, see Extract Your Data.
Reference: https://help.tableau.com/current/pro/desktop/en-us/environ_filesandfolders.htm
Question 57
Which of the following are valid Layout Container types when using Dashboards in Tableau?
Correct Answer:AC
Reference: 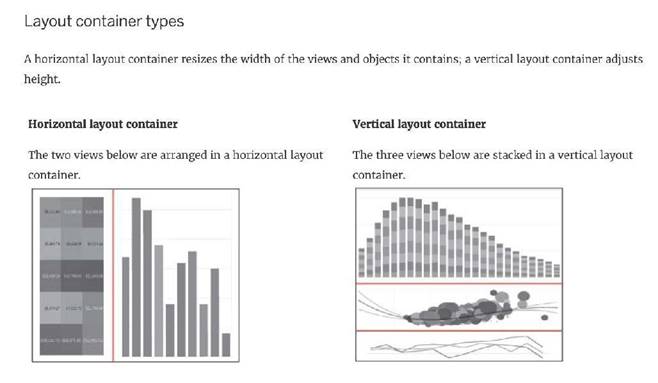
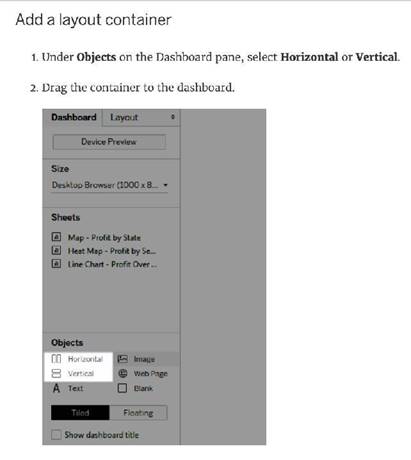
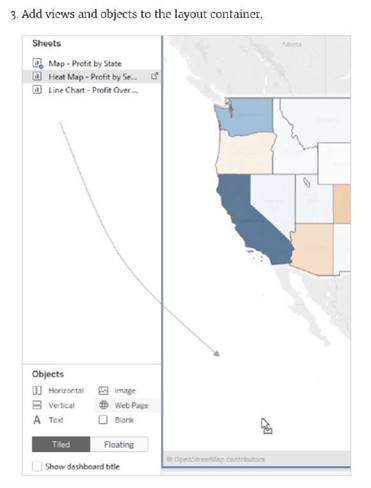
https://help.tableau.com/current/pro/desktop/en-us/dashboards_organize_floatingandtiled.htm
Question 58
Which of the following are true about Dashboards in Tableau?
Correct Answer:ABC
From the official Tableau documentation:
As we can see below, Bar charts can be used as a floating object.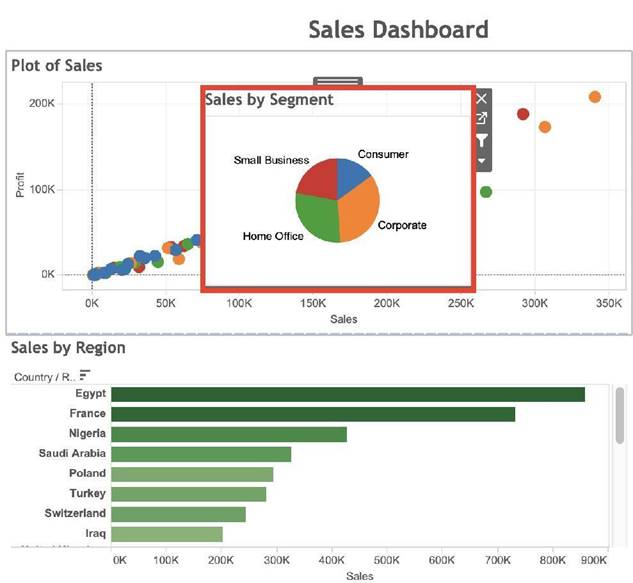
Reference: https://help.tableau.com/current/pro/desktop/en- us/dashboards_organize_floatingandtiled.htm
Question 59
The Shape option is available for which two views? Choose two.
Correct Answer:BD
The Shape option is available for scatter plots and packed bubbles views. The Shape option allows you to change the shape of marks in the view by selecting from a predefined set of shapes or adding custom shapes. You can access the Shape option by placing any field on Shape on the Marks card4 Scatter plots are views that show the relationship between two numerical variables by plotting them as coordinates on a Cartesian plane. You can create a scatter plot by placing at least one measure on Columns and at least one measure on Rows on the Marks card. You can then use Shape to assign different shapes to different categories or segments in your data5 Packed bubbles are views that show hierarchical data as a set of nested circles. Each circle represents a dimension member and its size is proportional to a measure value. You can create a packed bubble chart by placing one or more dimensions on Detail and one measure on Size on the Marks card. You can then use Shape to change the shape of circles to other shapes such as squares or stars6 The other options are not valid views for using the Shape option. Side-by-side circles are views that show proportions of a whole by using circles with different angles and sizes arranged horizontally or vertically. You can create a side-by-side circle chart by placing one dimension on Columns or Rows and one measure on Angle and Size on the Marks card. You cannot use Shape to change the shape of circles in this view7 Heat maps are views that show the distribution of two or more measures by using a color gradient and size. You can create a heat map by placing one or more dimensions on Columns and Rows and two measures on Color and Size on the Marks card. You cannot use Shape to change the shape of marks in this view8
Question 60
In an extract, what are three differences between a full refresh versus an incremental refresh? Choose three.
Correct Answer:ADE
According to the [Tableau Desktop Specialist Exam Guide], an incremental refresh only adds rows that are new, based on a specified column and value. A full refresh replaces all the extracted data with the data in the underlying data source. A full refresh is usually very slow, especially for large extracts. An incremental refresh can take less time, depending on how many new rows are added. A full refresh does not need to be configured, it is the default option for extracts in Tableau. An incremental refresh can be run from both Tableau Desktop and Tableau Server.