Online OGEA-101 Practice TestMore The-Open-Group Products >
Free The-Open-Group OGEA-101 Exam Dumps Questions
The-Open-Group OGEA-101: TOGAF Enterprise Architecture Part 1 Exam (English)
- Get instant access to OGEA-101 practice exam questions
- Get ready to pass the TOGAF Enterprise Architecture Part 1 Exam (English) exam right now using our The-Open-Group OGEA-101 exam package, which includes The-Open-Group OGEA-101 practice test plus an The-Open-Group OGEA-101 Exam Simulator.
- The best online OGEA-101 exam study material and preparation tool is here.
Question 1
Complete the sentence. The key purpose of Gap Analysis is to
Correct Answer:B
Gap Analysis is a technique that compares the Baseline Architecture and the Target Architecture to identify the differences and gaps between them. The purpose of this technique is to determine the changes and additions that are required to achieve the desired future state of the architecture. One of the main aspects of Gap Analysis is to identify the functions that aremissing or overlapping in the current and future architectures, and to plan how to address them. This helps to ensure that the architecture is complete, consistent, and aligned with the business objectives and requirements3
Question 2
Which of the following are the four purposes that typically frame the planning horizon, depth and breadth of an Architecture Project, and the contents of the EA Repository-?
Correct Answer:D
Strategy Portfolio Project Solution Delivery are the four purposes that typically frame the planning horizon, depth and breadth of an Architecture Project, and the contents of the EA Repository. They correspond to different levels of abstraction and granularity in the architecture development process. Reference: The TOGAF® Standard, Version 9.2 - The Open Group, Section 2.4 Architecture Repository.
Question 3
Consider the following ADM phases objectives.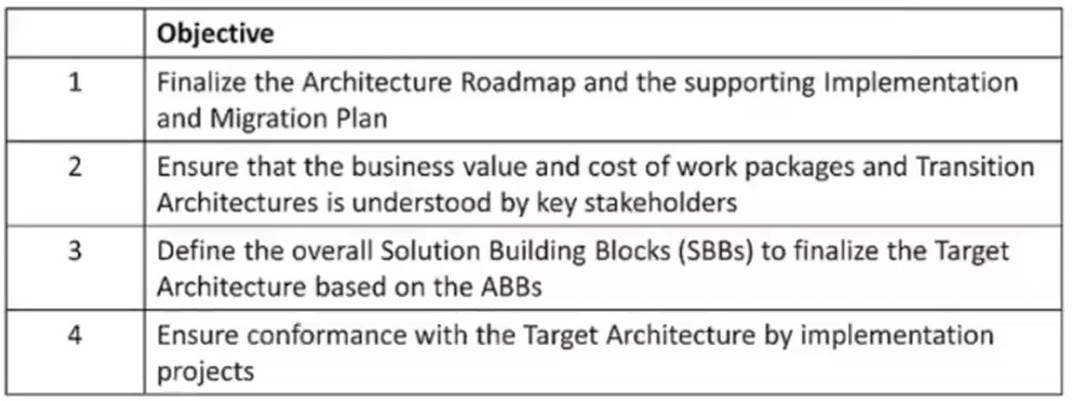
Which phase does each objective match?
Correct Answer:B
1E: To identify delivery vehicles (projects programs portfolios) that will deliver the Target Architecture 2F: To confirm readiness and ability to undergo change 3E: To determine whether an incremental approach is required and if so identify Transition Architectures that will deliver continuous business value 4G: To perform appropriate governance functions while the solution is being implemented
Reference: The TOGAF® Standard | The Open Group Website, Section 3.2 ADM Phases.
Question 4
What is present in all phases within the ADM and should be identified, classified and mitigated before starting a transformation effort?
Correct Answer:B
According to the TOGAF Standard, 10th Edition, risk is present in all phases within the Architecture Development Method (ADM), and it should be identified, classified, and mitigated before starting a transformation effort 1. Risk is defined as ??the effect of uncertainty on objectives?? 2, and it can have positive or negative impacts on the architecture project. Risk management is a technique that helps to assess and address the potential risks that may affect the achievement of the architecture objectives, and to balance the trade-offs between opportunities and threats. Risk management is applied throughout the ADM cycle, from the Preliminary Phase to the Requirements Management Phase, and it is integrated with other techniques, such as stakeholder management, business transformation readiness assessment, gap analysis, and migration planning 1. The other options are not correct, as they are not present in all phases within the ADM, and they are not necessarily identified, classified, and mitigated before starting a transformation effort. Budgetary constraints are the limitations on the financial resources available for the architecture project, and they are usually considered in Phase E: Opportunities and Solutions, and Phase F: Migration Planning 3. Schedule constraints are the limitations on the time available for the architecture project, and they are also usually considered in Phase E and F 3. Information gaps are the missing or incomplete data or knowledge that may affect the architecture project, and they are usually identified in Phase B: Business Architecture, Phase C: Information Systems Architecture, and Phase D: Technology Architecture . References: 1: TOGAF Standard, 10th Edition, Part III: ADM Guidelines and Techniques, Chapter 32: Risk Management. 2: TOGAF Standard, 10th Edition, Part I: Introduction, Chapter 3: Definitions. 3: TOGAF Standard, 10th Edition, Part II: Architecture Development Method, Chapter 16: Phase E: Opportunities and Solutions, and Chapter 17: PhaseF: Migration Planning. : TOGAF Standard, 10th Edition, Part II: Architecture Development Method, Chapter 13: Phase B: Business Architecture, Chapter 14: Phase C: Information Systems Architecture, and Chapter 15: Phase D: Technology Architecture.
Question 5
Consider the following statements.
* 1. All processes, decision-making, and mechanisms used will be established so as to minimize or avoid potential conflicts of interest.
* 2. More effective strategic decision-making will be made by C-Level executives and business leaders.
* 3. All actions implemented and their decision support will be available for inspection by authorized organization and provider parties.
* 4. Digital Transformation and operations will be more effective and efficient.
Which statements highlight the value and necessity for Architecture Governance to be adopted within organizations?
Correct Answer:B
Statements 1 and 3 highlight the value and necessity for Architecture Governance to be adopted within organizations. Architecture Governance is the practice and orientation by which Enterprise Architectures and other architectures are managed and controlled at an enterprise-wide level12. It ensures that architectural decisions are aligned with the organization??s strategy, objectives, and standards. Architecture Governance also involves establishing and maintaining processes, decision-making, and mechanisms to avoid or minimize potential conflicts of interest, such as between different stakeholders, business units, or projects34. Moreover, Architecture Governance requires transparency
and accountability for all actions implemented and their decision support, so that they can be inspected and evaluated by authorized parties, such as auditors, regulators, or customers5 . References:
•The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Architecture Governance - The Open Group
•Architecture Governance - The Open Group
•Tutorial: Governance in TOGAF??s Architecture Development Method (ADM)
•Architecture Governance in TOGAF: Ensuring Effective Management and Compliance
•The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Definitions - The Open Group
•[Architecture Governance in TOGAF: Ensuring Alignment and Control]
Question 6
Complete the following sentence. In the ADM, documents which are under development and have not undergone any formal review and approval process are called Documents which have been reviewed and approved are called
Correct Answer:B
According to the TOGAF Standard, 10th Edition, documents which are under development and have not undergone any formal review and approval process are called draft documents, while documents which have been reviewed and approved are called approved documents 1. Draft documents are typically marked with a version number of 0.x, indicating that they are incomplete or provisional. Approved documents are typically marked with a version number of 1.0 or higher, indicating that they have been finalized and authorized. The other options are not correct, as they are not the terms used by the TOGAF Standard to distinguish between documents under development and documents that have been reviewed and approved. The terms ??finalized??, ??concept??, ??deliverable??, and ??Version 0.1?? and ??Version 1.0?? are not specific to the TOGAF Standard, and they may have different meanings or interpretations in different contexts. References: 1: TOGAF Standard, 10th Edition, Part II: Architecture Development Method, Chapter 7: Applying Iteration to the ADM, Section 7.2.3 Document Categorization.