Question 13
Exhibit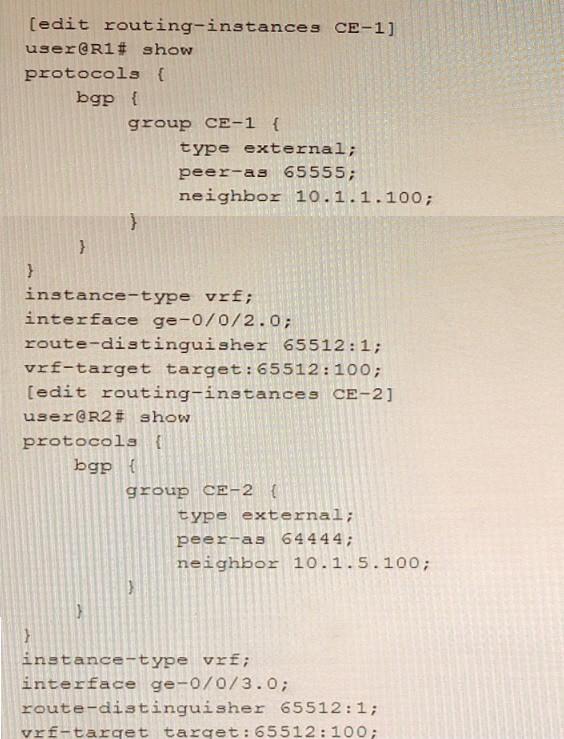
Referring to the exhibit, which statement is correct?
Correct Answer:C
The route distinguisher (RD) is a BGP attribute that is used to create unique VPN IPv4 prefixes for each VPN in an MPLS network. The RD is a 64-bit value that consists of two parts: an administrator field and an assigned number field. The administrator field can be an AS number or an IP address, and the assigned number field can be any arbitrary value chosen by the administrator. The RD is prepended to the IPv4 prefix to create a VPN IPv4 prefix that can be advertised across the MPLS network without causing any overlap or conflict with other VPNs. In this question, we have two PE routers (PE-1 and PE-2) that are connected to two CE devices (CE-1 and CE-2) respectively. PE-1 and PE-2 are configured with VRFs named Customer-A and Customer-B respectively.
Question 14
Exhibit
Which two statements about the configuration shown in the exhibit are correct? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:AD
The configuration shown in the exhibit is for a Layer 3 VPN that connects customer sites that use different AS numbers. A Layer 3 VPN is a type of VPN that uses MPLS labels to forward packets across a provider network and BGP to exchange routing information between PE routers and CE routers. A Layer 3 VPN allows customers to use different routing protocols and AS numbers at their sites, as long as they can peer with BGP at the PE-CE interface. In this example, CE-1 is using AS 65530 and CE-2 is using AS 65531, but they can still communicate through the VPN because they have BGP sessions with PE-1 and PE-2, respectively.
Question 15
Exhibit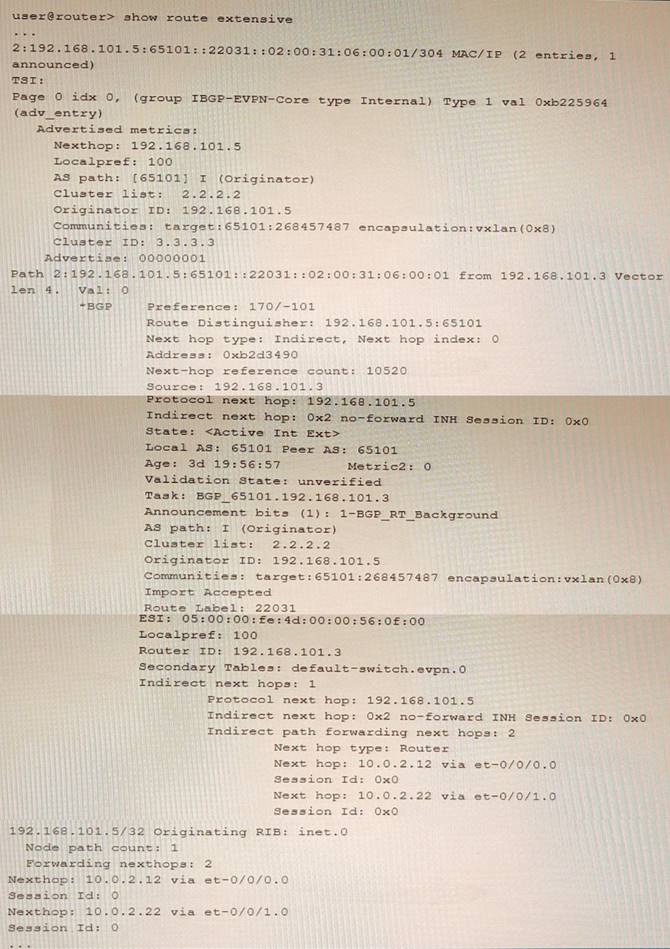
Referring to the exhibit, which two statements are true? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:BC
This is an EVPN Type-2 route, also called a MAC/IP advertisement route, that is used to advertise host IP and MAC address information to other VTEPs in an EVPN network. The route type field in the EVPN NLRI has a value of 2, indicating a Type-2 route. The device advertising this route into EVPN is 192.168.101.5, which is the IP address of the VTEP that learned the host information from the local CE device. This IP address is carried in the MPLS label field of the route as part of the VXLAN encapsulation.
Question 16
Which two statements are correct about the customer interface in an LDP-signaled pseudowire? (Choose two)
Correct Answer:CD
The customer interface in an LDP-signaled pseudowire is the interface on the PE router that connects to the CE device. An LDP-signaled pseudowire is a type of Layer 2 circuit that uses LDP to establish a point-to-point connection between two PE routers over an MPLS network. The customer interface can have different encapsulation types depending on the type of traffic that is carried over the pseudowire. The encapsulation types are ethernet-ccc, vlan-ccc, extended-vlan-ccc, atm-ccc, frame-relay- ccc, ppp-ccc, cisco-hdlc-ccc, and tcc-ccc. Depending on the encapsulation type, the customer interface can accept or reject tagged or untagged frames in the data plane, and include or exclude VLAN tags in the control plane LDP advertisement. The following table summarizes the behavior of different encapsulation types:
Question 17
Exhibit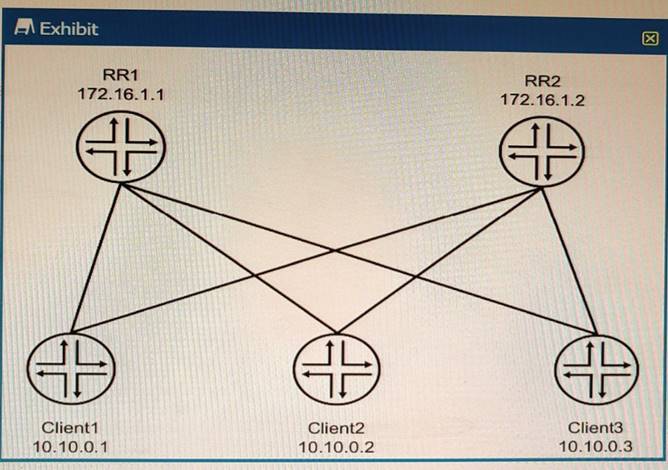
The environment is using BGP All devices are in the same AS with reachability redundancy Referring to the exhibit, which statement is correct?
Correct Answer:A
BGP route reflectors are BGP routers that are allowed to ignore the IBGP loop avoidance rule and advertise IBGP learned routes to other IBGP peers under specific conditions. BGP route reflectors can reduce the number of IBGP sessions and updates in a network by eliminating the need for a full mesh of IBGP peers. BGP route reflectors can have three types of peerings:
✑ EBGP neighbor: A BGP router that belongs to a different autonomous system (AS) than the route reflector.
✑ IBGP client neighbor: An IBGP router that receives reflected routes from the route reflector. A client does not need to peer with other clients or non-clients.
✑ IBGP non-client neighbor: An IBGP router that does not receive reflected routes from the route reflector. A non-client needs to peer with other non-clients and the route reflector.
In the exhibit, we can see that RR1 and RR2 are route reflectors in the same AS with reachability redundancy. They have two types of peerings: EBGP neighbors (R1 and R4) and IBGP client neighbors (Client1, Client2, and Client3). RR1 and RR2 are also peered with each other as IBGP non-client neighbors.