Question 7
You are configuring a BGP signaled Layer 2 VPN across your MPLS enabled core network. Your PE-2 device connects to two sites within the s VPN
In this scenario, which statement is correct?
Correct Answer:D
BGP Layer 2 VPNs use BGP to distribute endpoint provisioning information and set up pseudowires between PE devices. BGP uses the Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN) Routing Information Base (RIB) to store endpoint provisioning information, which is updated each time any Layer 2 virtual forwarding instance (VFI) is configured. The prefix and path information is stored in the L2VPN database, which allows BGP to make decisions about the best path.
In BGP Layer 2 VPNs, each site has a unique site ID that identifies it within a VFI. The site ID can be manually configured or automatically assigned by the PE device. By default, the site ID is automatically assigned based on the order that you add the interfaces to the site configuration. The first interface added to a site configuration has a site ID of 1, the second interface added has a site ID of 2, and so on.
Option D is correct because by default on PE-2, the remote site IDs are automatically assigned based on the order that you add the interfaces to the site configuration. Option A is not correct because by default on PE-2, the site’s local ID is automatically assigned a value of 0 and does not need to be configured to match the total number of attached sites. Option B is not correct because you do not need to create a unique Layer 2 VPN routing instance for each site on the PE-2 device. You can create one routing instance for all sites within a VFI. Option C is not correct because you do not need to use separate physical interfaces to connect PE-2 to each site. You can use subinterfaces or service instances on a single physical interface.
Question 8
Exhibit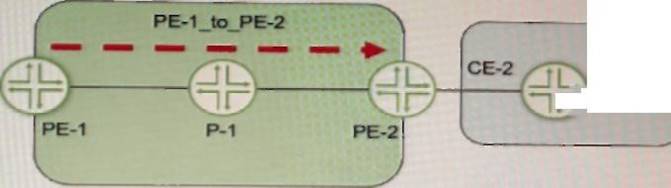
Referring to the exhibit, a working L3VPN exists that connects VPN-A sites CoS is configured correctly to match on the MPLS EXP bits of the LSP, but when traffic is sent from Site-1 to Site-2, PE-2 is not classifying the traffic correctly
What should you do to solve the problem?
Correct Answer:A
The explicit-null statement enables the PE router to send an MPLS label with a value of 0 (explicit null) instead of an IP header for packets destined to the VPN customer sites. This allows the penultimate hop router (the router before the egress PE router) to preserve the EXP bits of the MPLS label and pass them to the egress PE router. The egress PE router can then use these EXP bits to classify the traffic according to the CoS policy2. In this example, PE-1 should configure the explicit-null statement under [edit protocols mpls label-switched-path PE-1_to_PE-2] hierarchy level.
Question 9
Exhibit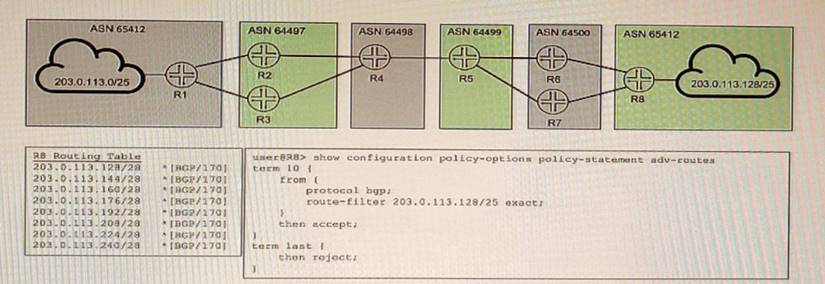
You are attempting to summarize routes from the 203.0.113.128/25 IP block on R8 to AS 64500. You implement the export policy shown in the exhibit and all routes from the routing table stop being advertised.
In this scenario, which two steps would you take to summarize the route in BGP? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:CD
To summarize routes from the 203.0.113.128/25 IP block on R8 to AS 64500, you need to do the following:
✑ Add the set routing-options static route 203.0.113.128/25 discard command. This creates a static route for the summary prefix and discards any traffic destined to it. This is necessary because BGP can only advertise routes that are present in the routing table.
✑ Replace exact in the export policy with orlonger. This allows R8 to match and advertise any route that is equal or more specific than the summary prefix. The exact term only matches routes that are exactly equal to the summary prefix, which is not present in the routing table.
Question 10
Exhibit
You want to use both links between R1 and R2 Because of the bandwidth difference between the two links, you must ensure that the links are used as much as possible.
Which action will accomplish this goal?
Correct Answer:D
VPLS is a Layer 2 VPN technology that allows multiple sites to connect over a shared IP/MPLS network as if they were on the same LAN. VPLS tunnels can be signaled using either Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) or Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). In this question, we have two links between R1 and R2 with different bandwidths (10 Gbps and 1 Gbps). We want to use both links as much as possible for VPLS traffic. To achieve this, we need to enable per-prefix load balancing on both routers. Per-prefix load balancing is a feature that allows a router to distribute traffic across multiple equal-cost or unequal- cost paths based on the destination prefix of each packet. This improves the utilization of multiple links and provides better load sharing than per-flow load balancing, which distributes traffic based on a hash of source and destination addresses4. Per-prefix load balancing can be enabled globally or per interface using the load-balance per-packet command.
Reference: 4: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/multiprotocol-label-switching-mpls/mpls/137544-technote-mpls-00.html
Question 11
You are responding to an RFP for a new MPLS VPN implementation. The solution must use LDP for signaling and support Layer 2 connectivity without using BGP The solution must be scalable and support multiple VPN connections over a single MPLS LSP The customer wants to maintain all routing for their Private network
In this scenario, which solution do you propose?
Correct Answer:C
AToM (Any Transport over MPLS) is a framework that supports various Layer 2 transport types over an MPLS network core. One of the transport types supported by AToM is LDP Layer 2 circuit, which is a point-to-point Layer 2 connection that uses LDP for signaling and MPLS for forwarding. LDP Layer 2 circuit can support Layer 2 connectivity without using BGP and can be scalable and efficient by using a single MPLS LSP for multiple VPN connections. The customer can maintain all routing for their private network by using their own CE switches.
Question 12
Which two statements are correct about IS-IS interfaces? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:BD
IS-IS supports two levels of routing: Level 1 (intra-area) and Level 2 (interarea). An IS-IS router can be either Level 1 only, Level 2 only, or both Level 1 and Level 2. A router that is both Level 1 and Level 2 is called a Level 1-2 router. A Level 1-2 router sends separate hello messages for each level on both point-to-point and broadcast interfaces1. A point-to-point interface provides a connection between a single source and a single destination. A broadcast interface behaves as if the router is connected to a LAN.