Question 7
How does OSPF calculate the best path to a particular prefix?
Correct Answer:A
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)calculates the best path based on thecostof the route, which is derived from the bandwidth of the interfaces along the path.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
OSPF Path Selection:
OSPF assigns a cost to each link, typically based on the link's bandwidth (higher bandwidth equals lower cost).
The OSPF algorithm computes the shortest path to a destination by adding the costs of all links in the path. The path with thenumerically lowest total costis chosen as the best path.
Cost Calculation:The OSPF cost can be manually adjusted or automatically calculated using the default formula:
Cost=Reference BandwidthLink Bandwidth\text{Cost} = \frac{\text{Reference Bandwidth}}{\text{Link Bandwidth}}Cost=Link BandwidthReference Bandwidth
Juniper Reference:
OSPF Best Path Selection: OSPF selects the path with the lowest cumulative cost, ensuring efficient use of higher-bandwidth links in Junos networks.
Question 8
Exhibit: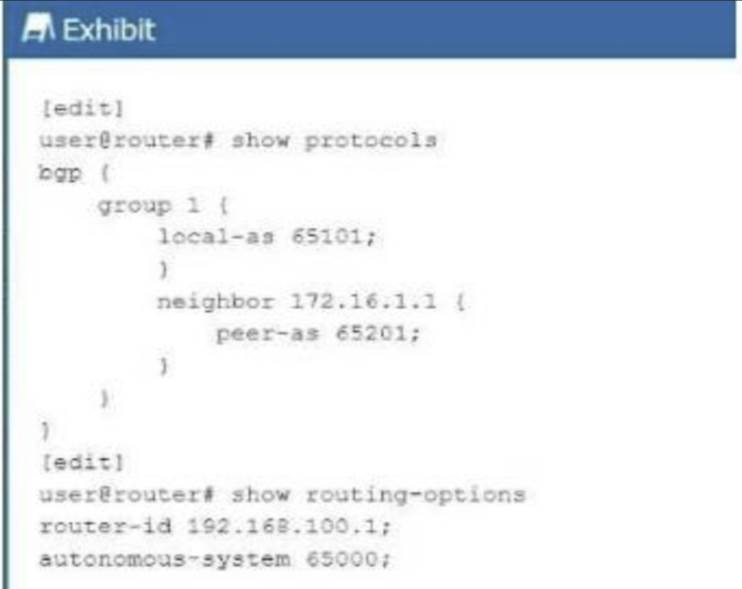
Referring to the exhibit, which statement is correct?
Correct Answer:B
In the exhibit, BGP is configured withlocal AS 65101and a neighbor at172.16.1.1inpeer AS 65201. This setup involves two different Autonomous Systems (AS), indicating anExternal BGP (EBGP)configuration.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:  EBGP vs. IBGP:
EBGP vs. IBGP: EBGPis used between routers in different ASes. In this case, the local AS is65101and the peer AS is65201, meaning the BGP session isEBGP.
EBGPis used between routers in different ASes. In this case, the local AS is65101and the peer AS is65201, meaning the BGP session isEBGP. IBGPis used between routers within the same AS, which is not applicable here as the AS numbers are different.
IBGPis used between routers within the same AS, which is not applicable here as the AS numbers are different. BGP Group Configuration:
BGP Group Configuration: The configuration does not require a type external parameter because Junos OSautomatically recognizes the session asEBGPwhen the local and peer AS numbers are different.
The configuration does not require a type external parameter because Junos OSautomatically recognizes the session asEBGPwhen the local and peer AS numbers are different. The BGP session will operate as EBGP, and the configuration will commit successfully.
The BGP session will operate as EBGP, and the configuration will commit successfully.
Juniper Reference: BGP Configuration: In Juniper, EBGP is automatically recognized when the local and peer AS numbers differ, without needing to specify type external.
BGP Configuration: In Juniper, EBGP is automatically recognized when the local and peer AS numbers differ, without needing to specify type external.
Question 9
What is the definition of a trunk interface on a switch?
Correct Answer:A
A trunk interface on a switch is used to carry traffic for multiple VLANs between switches or between a switch and another network device, like a router. Trunk interfaces use 802.1Q tagging to identify which VLAN the traffic belongs to.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
Trunk Ports:
Trunk ports are typically used for inter-switch links or switch-to-router links where multiple VLANs need to be carried over the same physical connection.
VLAN traffic is tagged with a VLAN ID to ensure that it is properly identified as it crosses the trunk link.
* 802.1Q VLAN Tagging:
Trunk ports use 802.1Q to tag Ethernet frames with the VLAN ID. This ensures that frames are correctly forwarded to the appropriate VLANs on the other side of the trunk.
Juniper Reference:
Trunk Interface Configuration: In Juniper switches, trunk ports are configured to carry tagged traffic for multiple VLANs, which is essential for interconnecting multiple network segments.
Question 10
Which statement is correct about an IRB interface?
Correct Answer:D
AnIRB (Integrated Routing and Bridging)interface provides routing functionality between VLANs at Layer 3, allowing devices in different VLANs to communicate with each other.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:  IRB Functionality:
IRB Functionality: The IRB interface enables routing between different VLANs by acting as a Layer 3 gateway.
The IRB interface enables routing between different VLANs by acting as a Layer 3 gateway.
Traffic within the same VLAN is handled by Layer 2 switching, while traffic between VLANs is routed through the IRB interface. Layer 3 Routing Between VLANs:
Layer 3 Routing Between VLANs: Each VLAN can be assigned an IP address on the IRB interface, which allows traffic to flow between VLANs based on Layer 3 IP routing.
Each VLAN can be assigned an IP address on the IRB interface, which allows traffic to flow between VLANs based on Layer 3 IP routing.
Juniper Reference: IRB Interface Configuration: Juniper supports IRB for inter-VLAN routing on devices like the EX and QFX series switches, facilitating Layer 3 communication in data centers.
IRB Interface Configuration: Juniper supports IRB for inter-VLAN routing on devices like the EX and QFX series switches, facilitating Layer 3 communication in data centers.
Question 11
Which two statements are correct about rules for EBGP and IBGP? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:AC
EBGP (External BGP)andIBGP (Internal BGP)operate with different rules due to the nature of their relationships.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
TTL Differences:
EBGP: By default, EBGP peers have a TTL of 1, meaning they must be directly connected, or the TTL needs to be manually increased for multihop EBGP.
IBGP: IBGP peers within the same AS have a TTL of 255, as they are expected to communicate over multiple hops within the AS.
Preference for EBGP Routes:
Routes learned viaEBGPare typically preferred over IBGP routes. This is because EBGP routes are considered more reliable since they originate outside the AS, while IBGP routes are internal.
Juniper Reference:
BGP Configuration: The different handling of TTL and route preferences between EBGP and IBGP ensures proper route selection and security within Junos-based networks.
Question 12
A routing policy has been created to advertise OSPF routes in BGP. Which statement is correct in this scenario?
Correct Answer:A
When advertisingOSPF routesintoBGP, the appropriaterouting policyshould be applied as anexport policyin BGP.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
OSPF to BGP Route Advertisement:Routes learned via OSPF (a dynamic IGP) need to be exported into BGP to be advertised to external BGP peers. In Junos OS, this is done usingexport policies.
Export Policies in BGP:An export policy controls which routes are advertised out of a BGP session. In this scenario, the routing policy must be applied toBGP as an export policyto export the OSPF-learned routes to external BGP peers.
Policy Configuration:Example configuration:
set policy-options policy-statement EXPORT_OSPF term 1 from protocol ospf
set policy-options policy-statement EXPORT_OSPF term 1 then accept
set protocols bgp group export EXPORT_OSPF
This policy ensures that only OSPF routes are exported into BGP.
Juniper Reference:
Routing Policy: Export policies are used in BGP to control route advertisements to peers, including those learned via OSPF.