Online JN0-105 Practice TestMore Juniper Products >
Free Juniper JN0-105 Exam Dumps Questions
Juniper JN0-105: Junos - Associate (JNCIA-Junos) 2024 Exam
- Get instant access to JN0-105 practice exam questions
- Get ready to pass the Junos - Associate (JNCIA-Junos) 2024 Exam exam right now using our Juniper JN0-105 exam package, which includes Juniper JN0-105 practice test plus an Juniper JN0-105 Exam Simulator.
- The best online JN0-105 exam study material and preparation tool is here.
Question 1
What will the request system configuration rescue save command do?
Correct Answer:A
The request system configuration rescue save command in Junos OS saves the most recently committed configuration as the rescue configuration. This rescue
configuration can be used to recover the device if future configurations cause issues. It ensures there is a stable, known-good configuration to fall back on, which is crucial in network management and troubleshooting.
References:
✑ "rescue : save configurations as the rescue: request system configuration save
.................( saves the current configs as a rescue configs )" from Useful Juniper Commands.txt.
✑ Juniper official documentation: Configuring and Activating a Rescue Configuration.
Question 2
Which two common routing policy actions affect the flow of policy evaluation? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:AC
In Junos OS routing policy evaluation, "next policy" (A) and "next term" (C) are common actions that affect the flow of policy evaluation. "Next policy" directs the evaluation to the next policy in the sequence, whereas "next term" moves the evaluation to the next term within the current policy, allowing for granular control over routing decisions.
Question 3
Click the Exhibit button.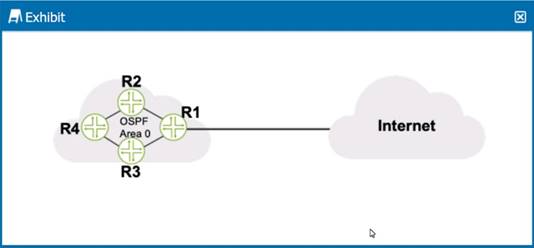
Referring to the exhibit, what should be configured on R1 to advertise a default static route into OSPF?
Correct Answer:B
To advertise a default static route into OSPF on router R1, a routing policy should be configured. This policy would typically include a statement to match the default route (0.0.0.0/0) and then apply an action to set the route as an OSPF external type, which would then be redistributed into the OSPF domain. The routing policy is a set of conditions and actions that determine how routes are imported into or exported from the routing table and how routes are shared between routing instances or routing protocols. After defining the policy, it must be applied to OSPF under the export section of the OSPF configuration on R1. This process will allow R1 to announce the default route to other OSPF routers in the network, which then can use it as a gateway of last resort to reach the Internet or other networks not explicitly known to the OSPF domain.
Question 4
Which criteria does the Junos OS use to select an active route when two entries exist in the routing table?
Correct Answer:A
In Junos OS, when two entries for the same destination exist in the routing table, the route with the lowest preference number is selected as the active route. This preference number, also known as the route preference or administrative distance, is used to prioritize routes received from different routing protocols.
Question 5
An administrator configures a router's interface with an IPv4 address and subnet mask. The administrator also confirms that this interface is in an up state.
In this scenario, which two route types are created on the local router? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:BD
When an interface on a router is configured with an IPv4 address and is in an up state, two types of routes are automatically created in the routing table: a local route and a direct route, making B and D the correct answers. The local route represents the interface's IP address itself, indicating that the router can directly receive packets addressed to this IP. The direct route represents the subnet or network segment to which the interface is connected, indicating that the router can directly forward packets to destinations within this subnet.
Question 6
What are two benefits when implementing class of service? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:C
Class of Service (CoS) in Junos OS provides tools for managing traffic congestion and ensuring that latency-sensitive traffic is given priority over less time-critical data. By implementing CoS, network administrators can classify traffic into different priority levels, apply scheduling policies to ensure that high-priority traffic is transmitted first, and use congestion management techniques such as queue buffers and drop profiles. This helps in maintaining the quality of service for critical applications, especially during periods of high network congestion. However, CoS does not eliminate congestion entirely nor does it inherently make the network faster; it provides a mechanism for better managing and controlling traffic flows according to their importance and time sensitivity.