Question 37
A software company decides to invest in reviews of various types. The thought process they have is that each artifact needs to be reviewed using only one of the review methods depending on the criticality of the artifact.
Correct Answer:C
The thought process of the software company is incorrect, because it assumes that each artifact can be reviewed using only one review method, and that the review method depends solely on the criticality of the artifact. This is a simplistic and rigid approach that does not consider the benefits and limitations of different review methods, the context and purpose of the review, and the feedback and improvement opportunities that can be gained from multiple reviews. According to the CTFL 4.0 Syllabus, the selection of review methods should be based on several factors, such as the type and level of detail of the artifact, the availability and competence of the reviewers, the time and budget constraints, the expected defects and risks, and the desired outcomes and quality criteria. Moreover, the same artifact can be reviewed using different review methods at different stages of the development lifecycle, to ensure that the artifact meets the changing requirements, standards, and expectations of the stakeholders. For example, a requirement specification can be reviewed using an informal review method, such as a walkthrough, to get an initial feedback from the users and developers, and then using a formal review method, such as an inspection, to verify the completeness, correctness, and consistency of the specification. Therefore, the software company should adopt a more flexible and context-sensitive approach to selecting and applying review methods for different artifacts, rather than following a fixed and arbitrary rule. References = CTFL 4.0 Syllabus, Section 3.2.1, page 31-32; Section 3.2.2, page 33-34; Section 3.2.3, page 35-36.
Question 38
Which of the following statements contradicts the general principles of testing?
Correct Answer:B
Statement B contradicts the general principles of testing, because running the same test set more often will not increase the chances of finding new defects, unless there are some changes in the system or environment that affect the test results. Running different test sets with different inputs, outputs or conditions would be more effective in finding new defects. Statements A, C and D are consistent with the general principles of testing. Statement A states that most defects are found in a small subset of a system’s modules, which is true according to the defect clustering principle. Statement C states that testing is better if it starts at the beginning of a project, which is true according to the early testing principle. Statement D states that how testing is done, is based on the situation in a particular project, which is true according to the context-dependent testing principle. Verified References: A Study Guide to the ISTQB® Foundation Level 2018 Syllabus - Springer, pages 4-6.
Question 39
Which type of software development product can undergo static testing?
Correct Answer:A
Static testing is a form of testing that does not involve executing the software, but rather analyzing it for defects, errors, or violations of standards. Static testing can be applied to any software development product, including requirements specifications, design specifications, code, test cases, test plans, user manuals, etc. Static testing can be done by using various techniques such as reviews, inspections, walkthroughs, checklists, static analysis tools, etc. Verified References: A Study Guide to the ISTQB® Foundation Level 2018 Syllabus - Springer, page 7.
Question 40
Which sequence of stated in the answer choices is correct in accordance with the following figure depicting the life-cycle of a defect?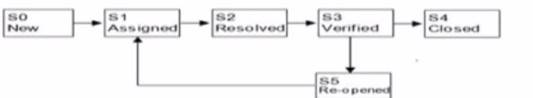
Correct Answer:D
According to the ISTQB Certified Tester Foundation Level (CTFL) v4.0, the life cycle of a defect typically follows a sequence from its discovery to its closure. In the provided figure, it starts with S0 (New), moves to S1 (Assigned), then to S2 (Resolved), followed by S3 (Verified). If the defect is not fixed, it can be Re-opened (S5) and goes back for verification (S3). Once verified, it is Closed (S4). References: ISTQB Certified Tester Foundation Level (CTFL) v4.0 Syllabus, Section 1.4.3, Page 17.
Question 41
Which of the following coverage criteria results in the highest coverage for state transition based test cases?
Correct Answer:B
Covering all transitions at least once is the highest coverage criterion for state transition based test cases, because it ensures that every possible change of state is tested at least once. This means that all the events that trigger the transitions, as well as the actions and outputs that result from the transitions, are verified. Covering all transitions at least once also implies covering all states at least once, but not vice versa. Therefore, option D is not the highest coverage criterion. Option C is the lowest coverage criterion, because it only tests the initial and final states of the system or component, without checking the intermediate states or transitions. Option A is incorrect, because the coverage criteria for state transition based test cases can be determined and compared based on the number of transitions and states covered. References = CTFL 4.0 Syllabus, Section 4.2.3, page 49-50.
Question 42
For withdrawing money tram an Automated Teller Machine (ATM), the following conditions are required:
- The bank card is valid
- The PIN code is correct
- Money is available in the user's account
The following are some possible interactions between the user and the ATM:
- The entered card is invalid The card is rejected
- The PIN code is wrong The ATM asks for another PIN code
- The requested amount is more than available in the user's account: The ATM asks for another amount
- The requested amount is available in the user's account The ATM dispenses the money Which test design technique should be used to cover all possible combinations of the in put conditions?
Correct Answer:B
A decision table is a technique that should be used to cover all possible combinations of input conditions for withdrawing money from an Automated Teller Machine (ATM). A decision table shows combinations of inputs and/or stimuli (causes) with their associated outputs and/or actions (effects). A decision table consists of four quadrants: conditions (inputs), actions (outputs), condition entries (values) and action entries (results). A decision table can be used to test components that have multiple inputs and outputs that depend on logical combinations of conditions. For example, for testing the ATM, we can identify three input conditions: the bank card is valid, the PIN code is correct, and money is available in the user’s account. We can also identify four output actions: the card is rejected, the ATM asks for another PIN code, the ATM asks for another amount, and the ATM dispenses the money. A decision table can show all possible combinations of these conditions and actions in a systematic way.
Use case based testing is not a technique that can cover all possible combinations of input conditions for withdrawing money from an ATM. Use case based testing is a technique that verifies that a software product or system meets its specified requirements or user stories by executing realistic scenarios or workflows. Use case based testing can be used to test components that have complex or dynamic interactions with users or other systems. For example, for testing the ATM, we can identify several use cases, such as withdraw money, check balance, transfer money, etc. Each use case can have one or more scenarios that describe the steps and outcomes of the interaction. However, use case based testing may not cover all possible combinations of input conditions, as some scenarios may be omitted or overlooked.
Boundary value analysis is not a technique that can cover all possible combinations of input conditions for withdrawing money from an ATM. Boundary value analysis is a technique that tests boundary values between partitions of equivalent data. Boundary values are values at the edge of an equivalence partition or at the smallest incremental distance on either side of an edge. Boundary value analysis can be used to test components that have input values that can be divided into partitions of equivalent data. For example, for testing the ATM, we can identify boundary values for the input amount, such as the minimum and maximum amount allowed by the system or the user’s account. However, boundary value analysis may not cover all possible combinations of input conditions, as some conditions may not have boundary values or may not be related to input values.
Equivalence class partitioning is not a technique that can cover all possible combinations of input conditions for withdrawing money from an ATM. Equivalence class partitioning is a technique that divides the input data and output results of a software component into partitions of equivalent data. Each partition should contain data that is treated in the same way by the component. Equivalence class partitioning can be used to test components that have input values that can be divided into partitions of equivalent data. For example, for testing the ATM, we can identify equivalence partitions for the input amount, such as valid amount (within the range allowed by the system and the user’s account) and invalid amount (outside the range allowed by the system or the user’s account). However, equivalence class partitioning may not cover all possible combinations of input conditions, as some conditions may not be related to input values or may have more than two partitions. Verified References: [A Study Guide to the ISTQB® Foundation Level 2018 Syllabus - Springer], Chapter 4, page 34-46.