Question 7
An administrator enabled workspace mode and now wants to delete an address object that is currently referenced in a firewall policy. Which two results can the administrator expect? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:CD
When operating in workspace mode on FortiManager 7.4, the administrator must understand how object references and deletions work:
✑ Option C- "FortiManager will not allow the administrator to delete a referenced
address object until they lock the ADOM":In workspace mode, all changes are managed within an Administrative Domain (ADOM) scope. When an object (like an address object) is referenced in a policy, FortiManager prevents its deletion to maintain configuration integrity. The ADOM must be locked by the administrator to make changes to any referenced objects. This locking mechanism ensures that no unintended deletions or changes occur that could disrupt the policies or configuration.
✑ Option D- "FortiManager will replace the deleted address object with the none
address object in the referenced firewall policy":If the administrator attempts to delete an address object that is currently referenced by a firewall policy, FortiManager will replace the deleted object with the 'none' address object. This is done to maintain the policy structure and avoid policy corruption due to a missing reference. This behavior ensures that the firewall policy remains syntactically correct, even though the specific address object is no longer in use.
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit.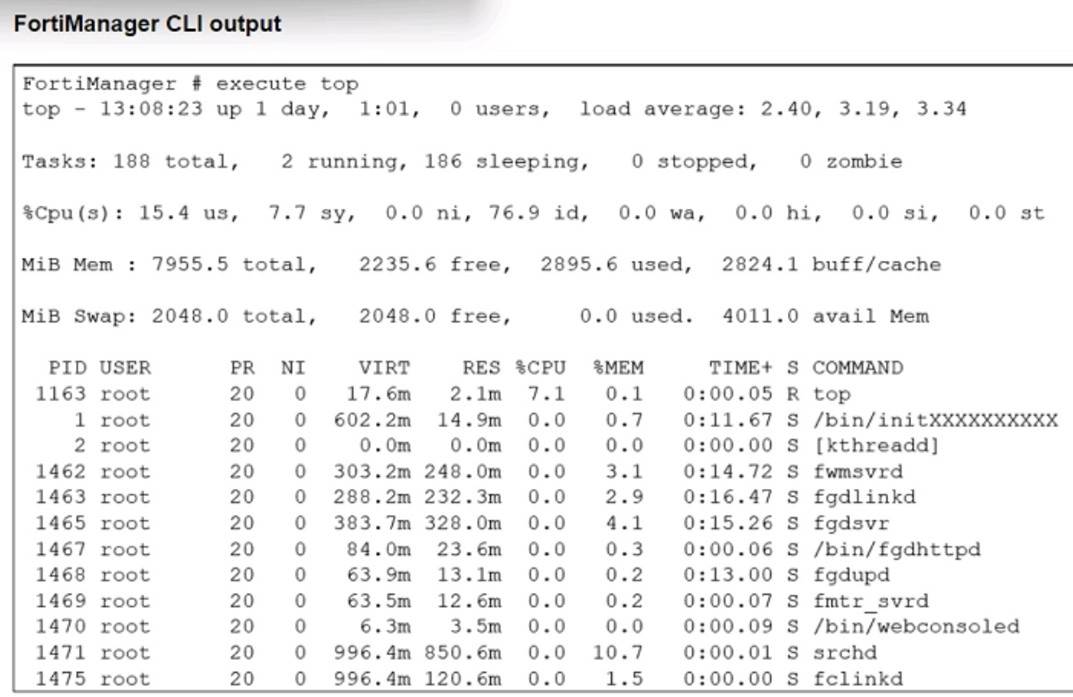
What percent of the available RAM is being used by the process in charge of downloading the web and email filter databases from the public FortiGuard servers?
Correct Answer:A
In the exhibit, the FortiManager CLI output displays the results of thetopcommand, which shows system processes, CPU usage, and memory (RAM) usage. We are specifically looking for the process responsible for downloading theweb and email filter databases from the public FortiGuard servers. This process is typically handled by thefgdlinkd process.
Key information from the output:
✑ Thefgdlinkdprocess is listed with aPID of 1463.
✑ The%MEMcolumn shows that this process is using2.9%of the available RAM.
Evaluation of Options:
✑ A. 2.9: This iscorrect. Thefgdlinkdprocess, which handles the web and email filter database downloads, is using2.9%of the available memory, as indicated in the%MEMcolumn.
✑ B. 3.1: This is incorrect. The3.1%memory usage belongs to thefwmsvrdprocess, not the fgdlinkd process.
✑ C. 1.5: This is incorrect. The1.5%memory usage belongs to thefclinkdprocess, not the fgdlinkd process.
✑ D. 4.1: This is incorrect. The4.1%memory usage belongs to thefgdsvrprocess, not the fgdlinkd process.
Question 9
In the event that one of the secondary FortiManager devices fails, which action must be performed to return the FortiManager HA manual mode to a working state?
Correct Answer:C
When a secondary FortiManager device fails in HA manual mode, an administrator must manually promote one of the working secondary devices to the primary role and reboot the old primary device to remove the peer IP of the failed device. This ensures the HA configuration is updated correctly, and the network remains resilient.
Options A, B, and D are incorrect because:
✑ A suggests the transition is transparent, which is true only in automatic mode, not in manual mode.
✑ B and D imply simpler steps that do not fully address the HA reconfiguration process in manual mode.
FortiManager References:
✑ Refer to FortiManager 7.4 High Availability (HA) Configuration Guide: Manual Mode Configuration and Failover Procedures.
Question 10
Which configuration setting for FortiGate is part o an ADOM-level database on FortiManager?
Correct Answer:B
✑ Option B: Routingis the correct answer. The ADOM-level database in FortiManager stores configuration settings such as routing, firewall policies, and objects that are shared across multiple devices in the ADOM.
Explanation of Incorrect Options:
✑ Option A: NSX-T Service Templateis incorrect as it is not a FortiGate-specific setting managed at the ADOM level.
✑ Option C: SNMPis incorrect because SNMP settings are typically managed on a per-device basis.
✑ Option D: Security profilesis incorrect because security profiles are generally device-level configurations, not ADOM-level.
FortiManager References:
✑ Refer to "FortiManager Administration Guide" for further details on ADOM-level and device-level configurations.
Question 11
Refer to the exhibit.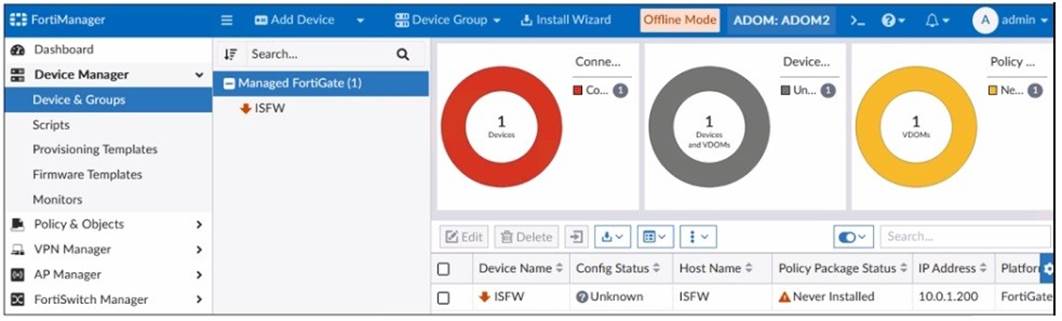
A junior administrator is troubleshooting a FortiManager connectivity issue that is occurring with a managed FortiGate device.
Given the FortiManager device manager settings shown in the exhibit, what can you conclude from this scenario?
Correct Answer:C
✑ Option C: The administrator can reclaim the FortiGate to FortiManager protocol (FGFM) tunnel to get the device online.This is the correct answer. The exhibit shows a device in "Unknown" status, which indicates that the FortiManager cannot currently communicate with the device. Reclaiming the FGFM tunnel will help to restore connectivity by re-establishing the management tunnel between the FortiManager and the FortiGate.
Explanation of Incorrect Options:
✑ Option A: The administrator must refresh the device to restore connectivityis incorrect because refreshing the device is unlikely to solve the connection issue when the status is "Unknown."
✑ Option B: FortiManager lost internet connectivity, therefore, the device appears to be downis incorrect because FortiManager does not require internet connectivity to manage a FortiGate; it needs a direct connection to the device.
✑ Option D: The administrator recently restored a FortiManager configuration fileis incorrect because the exhibit does not indicate a recent restoration of configuration.
FortiManager References:
✑ Refer to "FortiManager Administration Guide" and the section on "Device Management and Connectivity" for more information about reclaiming FGFM tunnels.