Online FCP_FGT_AD-7.4 Practice TestMore Fortinet Products >
Free Fortinet FCP_FGT_AD-7.4 Exam Dumps Questions
Fortinet FCP_FGT_AD-7.4: FCP - FortiGate 7.4 Administrator
- Get instant access to FCP_FGT_AD-7.4 practice exam questions
- Get ready to pass the FCP - FortiGate 7.4 Administrator exam right now using our Fortinet FCP_FGT_AD-7.4 exam package, which includes Fortinet FCP_FGT_AD-7.4 practice test plus an Fortinet FCP_FGT_AD-7.4 Exam Simulator.
- The best online FCP_FGT_AD-7.4 exam study material and preparation tool is here.
Question 1
Which three criteria can FortiGate use to look for a matching firewall policy to process traffic? (Choose
three.)
Correct Answer:ACE
• A. Services defined in the firewall policy: FortiGate uses the service specified in the firewall policy to match traffic. Services define the types of traffic (like HTTP, FTP) that the policy will apply to.
• C. Destination defined as Internet Services in the firewall policy: Policies can be matched based on the destination being categorized as Internet Services, allowing specific handling of such traffic.
• E. Source defined as Internet Services in the firewall policy: Similarly, traffic from sources categorized as Internet Services can be matched and processed according to the policy configuration.
Why the other options are less relevant:
• B. Highest to lowest priority defined in the firewall policy: Policies are processed from top to bottom, not by priority. The highest priority policy is processed first, but this is about the order of policy processing rather than criteria for matching traffic.
• D. Lowest to highest policy ID number: Policies are processed from the top of the list (the lowest policy ID) to the bottom (the highest policy ID), which is about the processing order rather than matching criteria.
Question 2
Refer to the exhibits.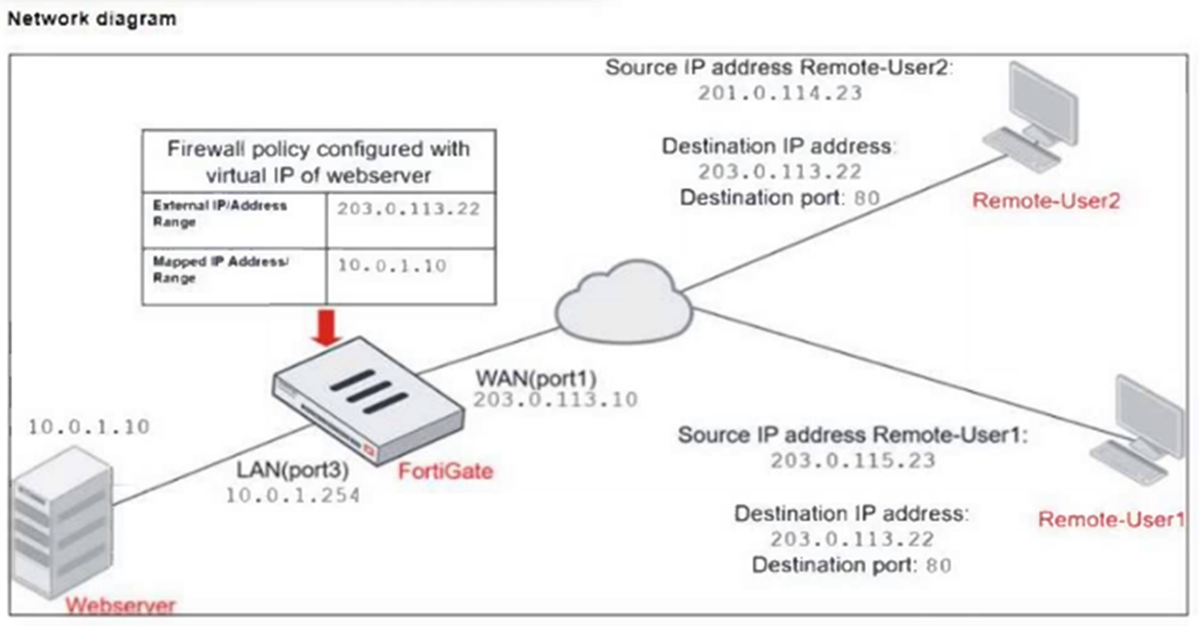
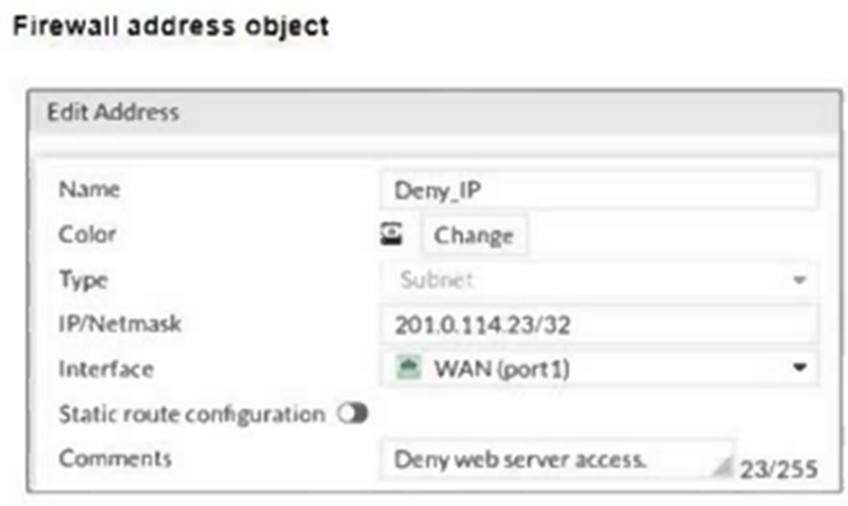

The exhibits show a diagram of a FortiGate device connected to the network, and the firewall configuration.
An administrator created a Deny policy with default settings to deny Webserver access for Remote-User2.
The policy should work such that Remote-User1 must be able to access the Webserver while preventing Remote-User2 from accessing the Webserver.
Which two configuration changes can the administrator make to the policy to deny Webserver access for Remote-User2? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:AB
Question 3
View the exhibit.
A user at 192.168.32.15 is trying to access the web server at 172.16.32.254.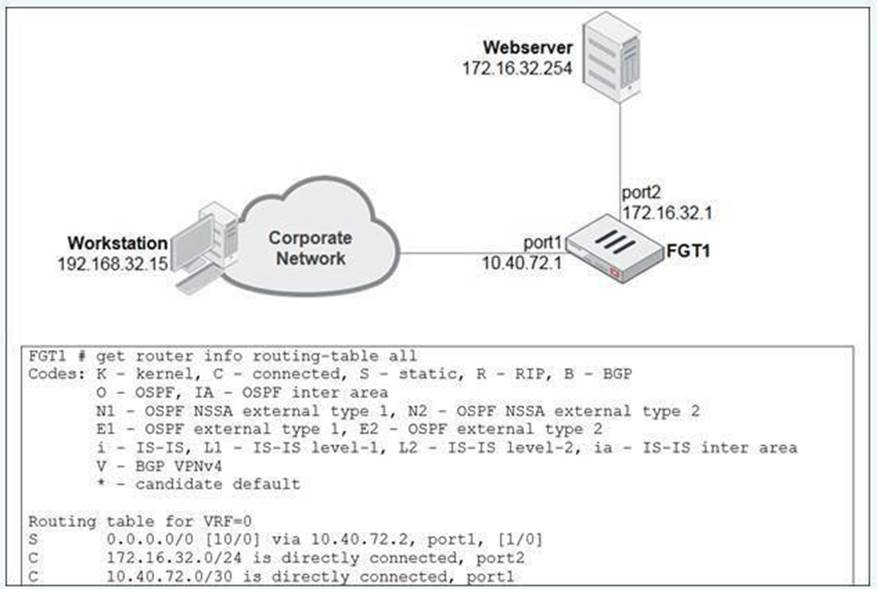
Which two statements best describe how the FortiGate will perform reverse path forwarding (RPF)
checks on this traffic? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:BC
When FortiGate performs reverse path forwarding (RPF) checks, it can operate in two modes: Strict
RPF and Loose RPF. Here??s how these two checks work:
In strict RPF, FortiGate checks whether the best route back to the source IP of the packet (in this
case, 192.168.32.15) goes through the same interface on which the packet was received. If the best
return path uses a different interface, the packet is denied. Based on the scenario:
o C. Strict RPF check will allow the traffic:
If the return path for 192.168.32.15 matches the interface where the traffic was received, the strict RPF check will allow the traffic.
• Loose RPF Check:
In loose RPF, FortiGate only checks if there is any route back to the source IP of the packet, regardless of the interface. This is a more permissive check, and if a route exists, the packet will be allowed.
o B. Loose RPF check will allow the traffic:
Since loose RPF requires only that a valid route to the source exists, the traffic is allowed.
Why the other options are less appropriate:
• A. Strict RPF check will deny the traffic:
This would only happen if the return route didn??t match the incoming interface, which is not indicated
here.
• D. Loose RPF check will deny the traffic:
Loose RPF is more permissive, so it will not deny the traffic as long as a valid route to the source IP exists.
Question 4
An administrator manages a FortiGate model that supports NTurbo. How does NTurbo enhance performance for flow-based inspection?
Correct Answer:A
NTurbo enhances performance for flow-based inspection by offloading traffic to the content processor.
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit.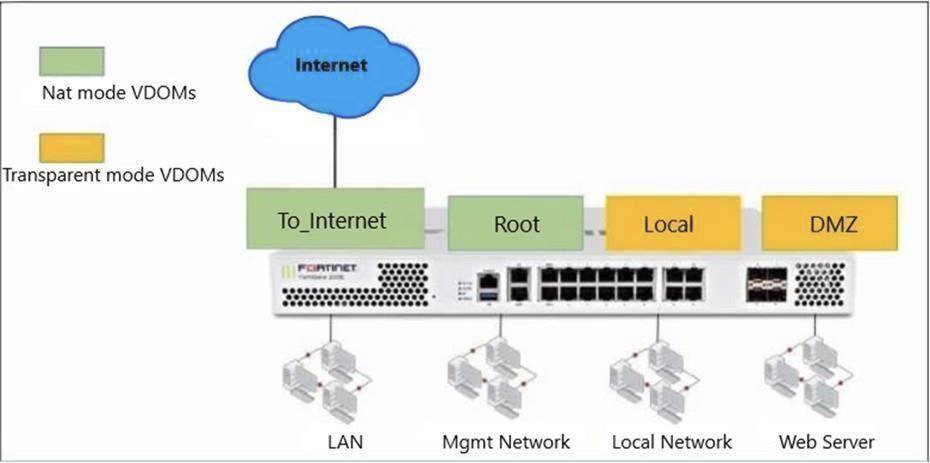
The Root and To_Internet VDOMs are configured in NAT mode. The DMZ and Local VDOMs are configured in transparent mode.
The Root VDOM is the management VDOM. The To_Internet VDOM allows LAN users to access the internet. The To_Internet VDOM is the only VDOM with internet access and is directly connected to ISP modem.
With this configuration, which statement is true?
Correct Answer:A
In this scenario, multiple Virtual Domains (VDOMs) are used, and each VDOM operates either in NAT mode or transparent mode:
• Root VDOM (management) and To_Internet VDOM are in NAT mode.
• DMZ VDOM and Local VDOM are in transparent mode.
To allow traffic between different VDOMs (e.g., Local and Root), inter-VDOM links must be configured.
Since Local VDOM is in transparent mode, it functions at Layer 2, meaning it requires an inter-VDOM link to pass traffic through the Root VDOM, which operates in NAT mode at Layer 3.
Why the other options are less appropriate:
• B. A default static route is not required on the To_Internet VDOM:
A default route is required on the To_Internet VDOM to send traffic from LAN users to the internet.
• C. Inter-VDOM links are required to allow traffic between the Local and DMZ VDOMs:
Both Local and DMZ are in transparent mode and operate at Layer 2, so direct communication
would require inter-VDOM links if passing through another VDOM.
• D. Inter-VDOM links are not required between the Root and To_Internet VDOMs:
Even if the Root VDOM is only used for management, it still requires inter-VDOM links to communicate with other VDOMs (like To_Internet) in the Security Fabric.
Question 6
What is the primary FortiGate election process when the HA override setting is disabled?
Correct Answer:A
When the HA override setting is disabled, FortiGate uses the primary election process based on the following criteria: Connected monitored ports: The unit with the most monitored ports up is preferred.
Connected monitored ports: The unit with the most monitored ports up is preferred. Priority: The unit with the highest priority is preferred.
Priority: The unit with the highest priority is preferred. System uptime: The unit with the longest uptime is preferred.
System uptime: The unit with the longest uptime is preferred. FortiGate serial number: Used as the final criterion to break any remaining ties.
FortiGate serial number: Used as the final criterion to break any remaining ties.
References: FortiOS 7.4.1 Administration Guide: HA election process
FortiOS 7.4.1 Administration Guide: HA election process