Question 97
- (Exam Topic 6)
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription 1 that contains two Azure virtual networks named VNet1 and VNet2. VNet1 contains a VPN gateway named VPNGW1 that uses static routing. There is a site-to-site VPN connection between your on-premises network and VNet1.
On a computer named Client1 that runs Windows 10, you configure a point to site VPN connection to VNet1. You configure virtual network peering between VNet1 and VNet2. You verify that you can connect to VNet2
from the on premises network. Client1 is unable to connect to VNet2.
You need to ensure that you can connect Client1 to VNet2. What should you do?
Correct Answer:C
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/vpn-gateway/vpn-gateway-about-point-to-site-routing
Question 98
- (Exam Topic 6)
You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources shown in the following table.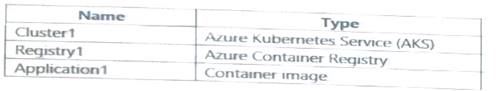
You need to deploy Application1 to Cluster1. Which command should you run?
Correct Answer:A
Question 99
- (Exam Topic 5)
You have an Azure subscription.
You have an on-premises virtual machine named VM1. The settings for VM1 are shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)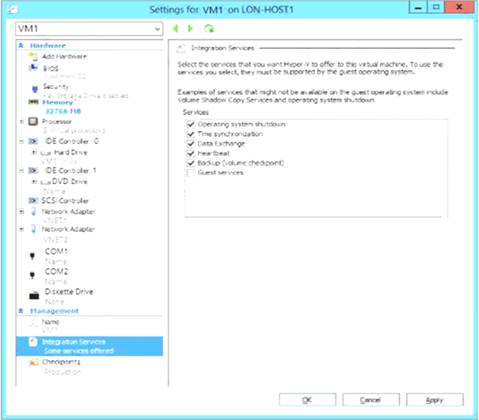
You need to ensure that you can use the disks attached to VM1 as a template for Azure virtual machines. What should you modify on VM1?
Correct Answer:D
From the exhibit we see that the disk is in the VHDX format.
Before you upload a Windows virtual machines (VM) from on-premises to Microsoft Azure, you must prepare the virtual hard disk (VHD or VHDX). Azure supports only generation 1 VMs that are in the VHD file format and have a fixed sized disk. The maximum size allowed for the VHD is 1,023 GB. You can convert a generation 1 VM from the VHDX file system to VHD and from a dynamically expanding disk to fixed-sized.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/windows/prepare-for-upload-vhd-image?toc=/azure
Question 100
- (Exam Topic 6)
You have an Azure virtual machine named VM1 that connects to a virtual network named VNet1. VM1 has
the following configurations:  Subnet: 10.0.0.0/24
Subnet: 10.0.0.0/24 Availability set: AVSet
Availability set: AVSet Network security group (NSG): None
Network security group (NSG): None  Private IP address: 10.0.0.4 (dynamic)
Private IP address: 10.0.0.4 (dynamic) Public IP address: 40.90.219.6 (dynamic)
Public IP address: 40.90.219.6 (dynamic)
You deploy a standard, Internet-facing load balancer named slb1. You need to configure slb1 to allow connectivity to VM1.
Which changes should you apply to VM1 as you configure slb1? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Solution:
Box 1: Remove the public IP address from VM1
If the Public IP on VM1 is set to Dynamic, that means it is a Public IP with Basic SKU because Public IPs with Standard SKU have Static assignments by default, that cannot be changed. We cannot associate Basic SKUs IPs with Standard SKUs LBs. One cannot create a backend SLB pool if the VM to be associated has a
Public IP. For Private IP it doesn't matter weather it is dynamic or static, still we can add the such VM into the SLB backend pool.
Box 2: Create and configure an NSG
Standard Load Balancer is built on the zero trust network security model at its core. Standard Load Balancer secure by default and is part of your virtual network. The virtual network is a private and isolated network. This means Standard Load Balancers and Standard Public IP addresses are closed to inbound flows unless opened by Network Security Groups. NSGs are used to explicitly permit allowed traffic. If you do not have an NSG on a subnet or NIC of your virtual machine resource, traffic is not allowed to reach this resource. To learn more about NSGs and how to apply them for your scenario, see Network Security Groups. Basic Load Balancer is open to the internet by default.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/load-balancer/quickstart-load-balancer-standard-public-portal https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/load-balancer/load-balancer-overview
Does this meet the goal?
Correct Answer:A
Question 101
- (Exam Topic 5)
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure subscription that contains 10 virtual networks. The virtual networks are hosted in separate resource groups.
Another administrator plans to create several network security groups (NSGs) in the subscription.
You need to ensure that when an NSG is created, it automatically blocks TCP port 8080 between the virtual networks.
Solution: From the Resource providers blade, you unregister the Microsoft.ClassicNetwork provider. Does this meet the goal?
Correct Answer:B
You should use a policy definition. Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-policy/policy-definition
Question 102
- (Exam Topic 5)
Your company has three offices. The offices are located in Miami, Los Angeles, and New York. Each office contains a datacenter.
You have an Azure subscription that contains resources in the East US and West US Azure regions. Each region contains a virtual network. The virtual networks are peered.
You need to connect the datacenters to the subscription. The solution must minimize network latency between the datacenters.
What should you create?
Correct Answer:A
Azure Virtual WAN is a networking service that brings many networking, security, and routing functionalities together to provide a single operational interface.
The Virtual WAN architecture is a hub and spoke architecture with scale and performance built in for branches (VPN/SD-WAN devices), users (Azure VPN/OpenVPN/IKEv2 clients), ExpressRoute circuits, and virtual networks.
Azure regions serve as hubs that you can choose to connect to. All hubs are connected in full mesh in a Standard Virtual WAN making it easy for the user to use the Microsoft backbone for any-to-any (any spoke) connectivity.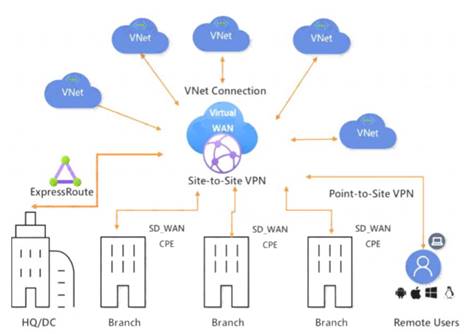
Virtual WAN offers the following advantages:
Integrated connectivity solutions in hub and spoke: Automate site-to-site configuration and connectivity between on-premises sites and an Azure hub.
Automated spoke setup and configuration: Connect your virtual networks and workloads to the Azure hub seamlessly.
Intuitive troubleshooting: You can see the end-to-end flow within Azure, and then use this information to take required actions.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-wan/virtual-wan-about