Question 13
Which CLI command does an NSX administrator run on the NSX Manager to generate support bundle logs if the NSX UI Is inaccessible?
Correct Answer:D
To generate the support bundle logs on the NSX Manager via API, the NSX administrator needs to use the POST method with the URL https://nsxmgr_ip/api/1.0/appliance-management/techsupportlogs/NSX, where nsxmgr_ip is the IP address of the NSX Manager1. This will create a tech support bundle file with a name like vcpnv.tgz. To download the generated tech support bundle file via CLI, the NSX administrator needs to use the get support-bundle file vcpnv.tgz command on the NSX Manager1. The other commands are incorrect because they either do not generate or download the support bundle logs, or they are not related to the NSX Manager.
Question 14
Which VPN type must be configured before enabling a L2VPN?
Correct Answer:A
According to the VMware NSX Documentation, this VPN type must be configured before enabling a L2VPN. L2VPN stands for Layer 2 VPN and is a feature that allows you to extend your layer 2 network across different sites using an IPSec tunnel. Route-based IPSec VPN is a VPN type that uses logical router ports to establish IPSec tunnels between sites.
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX/4.1/administration/GUID-86C8D6BB-F185-46DC-828C-1E1876B8
Question 15
Which TraceFlow traffic type should an NSX administrator use tor validating connectivity between App and DB virtual machines that reside on different segments?
Correct Answer:B
Unicast is the traffic type that an NSX administrator should use for validating connectivity between App and DB virtual machines that reside on different segments. According to the VMware documentation1, unicast traffic is the traffic type that is used to send a packet from one source to one destination. Unicast traffic is the most common type of traffic in a network, and it is used for applications such as web browsing, email, file transfer, and so on2. To perform a traceflow with unicast traffic, the NSX administrator needs to specify the source and destination IP addresses, and optionally the protocol and related parameters1. The traceflow will show the path of the packet across the network and any observations or errors along the way3. The other options are incorrect because they are not suitable for validating connectivity between two specific virtual machines. Multicast traffic is the traffic type that is used to send a packet from one source to multiple destinations simultaneously2. Multicast traffic is used for applications such as video streaming, online gaming and group communication4. To perform a traceflow with multicast traffic, the NSX administrator needs to specify the source IP address and the destination multicast IP address1. Broadcast traffic is the traffic type that is used to send a packet from one source to all devices on the same subnet2. Broadcast traffic is used for applications such as ARP, DHCP, and network discovery. To perform a traceflow with broadcast traffic, the NSX administrator needs to specify the source IP address and the destination MAC address as FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF1. Anycast traffic is not a valid option, as it is not supported by NSX Traceflow. Anycast traffic is a traffic type that is used to send a packet from one source to the nearest or best destination among a group of devices that share the same IP address. Anycast traffic is used for applications such as DNS, CDN, and load balancing.
Question 16
Match the NSX Intelligence recommendations with their correct purpose.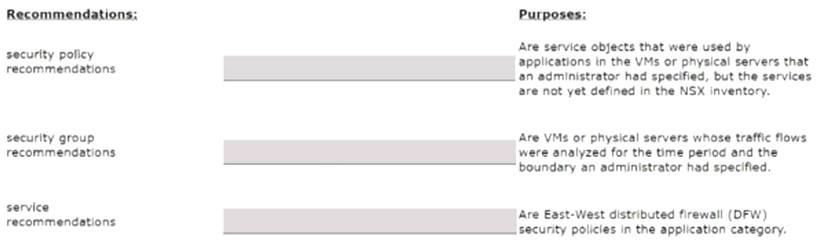
Solution: Security policy recommendations: Are East-West distributed firewall (DFW) security policies in the application category12.
Security policy recommendations: Are East-West distributed firewall (DFW) security policies in the application category12. Security group recommendations: Are VMs or physical servers whose traffic flows were analyzed for the time period and the boundary you had specified12.
Security group recommendations: Are VMs or physical servers whose traffic flows were analyzed for the time period and the boundary you had specified12. Service recommendations: Are service objects that were used by applications in the VMs or physical servers that you had specified, but the services are not yet defined in the NSX inventory12.
Service recommendations: Are service objects that were used by applications in the VMs or physical servers that you had specified, but the services are not yet defined in the NSX inventory12.
Does this meet the goal?
Correct Answer:A
Question 17
Which three selections are capabilities of Network Topology? (Choose three.)
Correct Answer:ABD
According to the VMware NSX Documentation, these are three of the capabilities of Network Topology, which is a graphical representation of your network infrastructure in NSX: Display how the different NSX components are interconnected: You can use Network Topology to view how your segments, gateways, routers, firewalls, load balancers, VPNs, and other NSX components are connected and configured in your network.
Display how the different NSX components are interconnected: You can use Network Topology to view how your segments, gateways, routers, firewalls, load balancers, VPNs, and other NSX components are connected and configured in your network. Display the uplink configured on the Tier-0 Gateways: You can use Network Topology to view the uplink interface and segment that connect your tier-0 gateways to your physical network. You can also view the VLAN ID and IP address of the uplink interface.
Display the uplink configured on the Tier-0 Gateways: You can use Network Topology to view the uplink interface and segment that connect your tier-0 gateways to your physical network. You can also view the VLAN ID and IP address of the uplink interface. Display the VMs connected to Segments: You can use Network Topology to view the VMs that are attached to your segments. You can also view the IP address and MAC address of each VM.
Display the VMs connected to Segments: You can use Network Topology to view the VMs that are attached to your segments. You can also view the IP address and MAC address of each VM.
Question 18
Which two statements are true for IPSec VPN? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:BC
According to the VMware NSX 4.x Professional documents and tutorials, IPSec VPN secures traffic flowing between two networks connected over a public network through IPSec gateways called endpoints. NSX Edge supports a policy-based or a route-based IPSec VPN. Beginning with NSX-T Data Center 2.5, IPSec VPN services are supported on both Tier-0 and Tier-1 gateways1. NSX Edge also leverages the DPDK accelerated performance library to optimize the performance of IPSec VPN2.