Question 7
Which CLI command shows syslog on NSX Manager?
Correct Answer:D
According to the VMware NSX CLI Reference Guide, this CLI command shows the syslog messages on the NSX Manager node. You can use this command to view the system logs for troubleshooting or monitoring purposes.
The other options are either incorrect or not available for this task. get log-file auth.log is a CLI command that shows the authentication logs on the NSX Manager node, not the syslog messages. /var/log/syslog/syslog.log is not a CLI command, but a file path that may contain syslog messages on some Linux systems, but not on the NSX Manager node. show log manager follow is not a valid CLI command, as there is no show log command or manager option in the NSX CLI.
## NSX Cli command get log-file
get log-file
# Below are commonly used log files, there are many more log files
get log-file
# use [follow] to continuing monitor Example: get log-file syslog follow get log-file syslog
Question 8
As part of an organization's IT security compliance requirement, NSX Manager must be configured for 2FA (two-factor authentication).
What should an NSX administrator have ready before the integration can be configured? O
Correct Answer:B
To configure NSX Manager for two-factor authentication (2FA), an NSX administrator must have VMware
Identity Manager (vIDM) with an OAuth Client added. vIDM provides identity management services and supports various 2FA methods, such as VMware Verify, RSA SecurID, and RADIUS. An OAuth Client is a configuration entity in vIDM that represents an application that can use vIDM for authentication and authorization. NSX Manager must be registered as an OAuth Client in vIDM before it can use
2FA. References: : VMware NSX-T Data Center Installation Guide, page 19. : VMware NSX-T Data Center Administration Guide, page 102. : VMware Blogs: Two-Factor Authentication with VMware NSX-T
Question 9
When collecting support bundles through NSX Manager, which files should be excluded for potentially containing sensitive information?
Correct Answer:C
According to the VMware NSX Documentation1, core files and audit logs can contain sensitive information and should be excluded from the support bundle unless requested by VMware technical support. Controller files and management files are not mentioned as containing sensitive information.
Question 10
Which statement is true about an alarm in a Suppressed state?
Correct Answer:D
The answer is D. An alarm can be suppressed for a specific duration in hours.
According to the VMware NSX documentation, an alarm can be in one of the following states: Open, Acknowledged, Suppressed, or Resolved12
An alarm in a Suppressed state means that the status reporting for this alarm has been disabled by the user for a user-specified duration12
When a user moves an alarm into a Suppressed state, they are prompted to specify the duration in hours. After the specified duration passes, the alarm state reverts to Open. However, if the system determines the condition has been corrected, the alarm state changes to Resolved13
To learn more about how to manage alarm states in NSX, you can refer to the following resources:  VMware NSX Documentation: Managing Alarm States 1
VMware NSX Documentation: Managing Alarm States 1 VMware NSX Documentation: View Alarm Information 2
VMware NSX Documentation: View Alarm Information 2 VMware NSX Intelligence Documentation: Manage NSX Intelligence Alarm States 3 https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX-Intelligence/1.2/user-guide/GUID-EBD3C5A8-F9AB-4A22-BA40-
VMware NSX Intelligence Documentation: Manage NSX Intelligence Alarm States 3 https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX-Intelligence/1.2/user-guide/GUID-EBD3C5A8-F9AB-4A22-BA40-
Question 11
Which command is used to display the network configuration of the Tunnel Endpoint (TEP) IP on a bare metal transport node?
Correct Answer:B
The command ifconfig is used to display the network configuration of the Tunnel Endpoint (TEP) IP on a ba metal transport node2. The TEP IP is assigned to a network interface on the bare metal server that is used for overlay traffic. The ifconfig command can show the IP address, netmask, broadcast address, and other information of the network interface. For example, the following command shows the network configuration
of the TEP IP on a bare metal transport node with interface name ens192:
ifconfig ens192
The output of the command would look something like this:
ens192: flags=4163
dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 234567 bytes 234567890 (234.5 MB) TX errors 0 dropped 0
overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
The TEP IP in this example is 10.10.10.10. References: IBM Cloud Docs
IBM Cloud Docs
Question 12
Refer to the exhibits.
Drag and drop the NSX graphic element icons on the left found in an NSX Intelligence visualization graph to Its correct description on the right.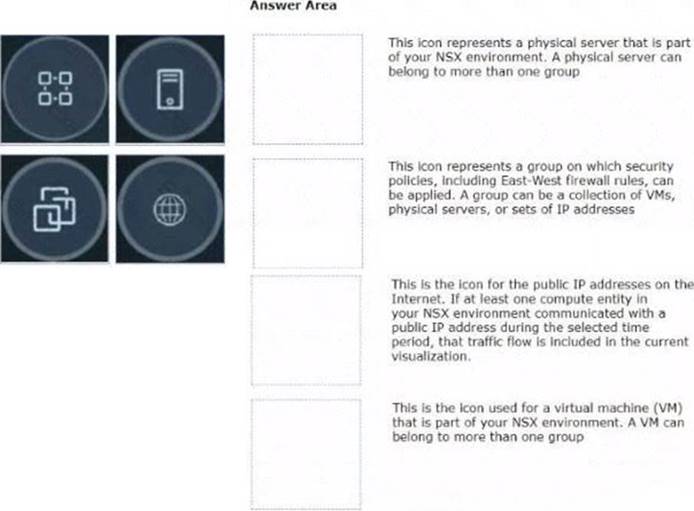
Solution:
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX-Intelligence/4.0/user-guide/GUID-DC78552B-2CC4-410D-A6C9-3
Does this meet the goal?
Correct Answer:A