Online 1Z0-821 Practice TestMore Oracle Products >
Free Oracle 1Z0-821 Exam Dumps Questions
Oracle 1Z0-821: Oracle Solaris 11 System Administrator
- Get instant access to 1Z0-821 practice exam questions
- Get ready to pass the Oracle Solaris 11 System Administrator exam right now using our Oracle 1Z0-821 exam package, which includes Oracle 1Z0-821 practice test plus an Oracle 1Z0-821 Exam Simulator.
- The best online 1Z0-821 exam study material and preparation tool is here.
Question 1
Which command would you use from the bash shell to determine the total amount of physical memory installed in your Solaris system (x86 and SPARC)?
Correct Answer:B
The prtconf command prints the system configuration information. The output includes the total amount of memory, and the configuration of system peripherals formatted as a device tree.
If a device path is specified on the command line for those command options that can take a device path, prtconf will only display information for that device node.
Question 2
View the exhibit.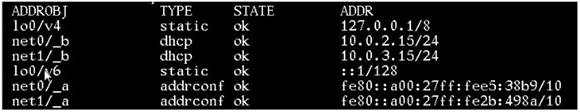
The configuration information in the exhibit is displayed on your system immediately after installing the OS.
Choose the option that describes the selection made during the Installation of the OS to obtain this configuration.
Correct Answer:A
There are two ways to configure the network configuration: automatic or manual.
In the exhibit we see that DHCP has been used used. This indicates an automatic network configuration.
Question 3
Select two correct statements about the authentication services available in Oracle Solaris 11.
Correct Answer:AE
A: Pluggable Authentication Modules (PAM) are an integral part of the authentication mechanism for the Solaris. PAM provides system administrators with the ability and flexibility to choose any authentication service available on a system to perform end-user authentication.
By using PAM, applications can perform authentication regardless of what authentication method is defined by the system administrator for the given client.
PAM enables system administrators to deploy the appropriate authentication mechanism for each service throughout the network. System administrators can also select one or multiple authentication technologies without modifying applications or utilities. PAM insulates application developers from evolutionary improvements to authentication technologies, while at the same time allowing deployed applications to use those improvements.
PAM employs run-time pluggable modules to provide authentication for system entry services.
E: The Simple Authentication and Security Layer (SASL) is a method for adding authentication support to connection-based protocols.
Simple Authentication and Security Layer (SASL) is a framework for authentication and data security in Internet protocols. It decouples authentication mechanisms from application protocols, in theory allowing any authentication mechanism supported by SASL to be used in any application protocol that uses SASL. Authentication mechanisms can also support proxy authorization, a facility allowing one user to assume the identity of another. They can also provide a data security layer offering data integrity and data confidentiality services. DIGEST-MD5 provides an example of mechanisms which can provide a data-security layer. Application protocols that support SASL typically also support Transport Layer Security (TLS) to complement the services offered by SASL.
Question 4
You have installed the SMF notification framework to monitor services. Which command is used to set up the notifications for a particular service?
Correct Answer:A
How to Set Up Email Notification of SMF Transition Events
This procedure causes the system to generate an email notification each time one of the services or a selected service has a change in state. You can choose to use either SMTP or SNMP. Normally, you would only select SNMP if you already have SNMP configured for some other reason.
By default, SNMP traps are sent on maintenance transitions. If you use SNMP for monitoring, you can configure additional traps for other state transitions.
1. Become an administrator or assume a role that includes the Service Management rights profile.'
2. Set notification parameters. Example 1:
The following command creates a notification that sends email when transactions go into the maintenance state.
# /usr/sbin/svccfg setnotify -g maintenance mailto:sysadmins@example.com
Example 2:
The following command creates a notification that sends email when the switch service goes into the online state.
# /usr/sbin/svccfg -s svc:/system/name-service/switch:default setnotify to-online \ mailto:sysadmins@example.com
Note: The svccfg command manipulates data in the service configuration repository. svccfg can be invoked interactively, with an individual subcommand, or by specifying a command file that contains a series of subcommands.
Changes made to an existing service in the repository typically do not take effect for that service until the next time the service instance is refreshed.
Question 5
A user account must be a member of a primary group, and may also be a member of one or more secondary groups. What is the maximum total number of groups that one user can concurrently belong to?
Correct Answer:B
Each user belongs to a group that is referred to as the user’s primary group. The GID number, located in the user’s account entry within the /etc/passwd file, specifies the user’s primary group.
Each user can also belong to up to 15 additional groups, known as secondary groups. In the /etc/group file, you can add users to group entries, thus establishing the user’s secondary group affiliations.
Note (4 PSARC/2009/542):
his project proposes changing the maximum value for NGROUPS_MAX from 32 to 1024 by changing the definition of NGROUPS_UMAX from 32 to 1024.
The use for a larger number of groups is described in CR 4088757, particular in the case of Samba servers and ADS clients; the Samba servers map every SID to a Unix group. Users with more than 32 groups SIDs are common. We've seen reports varying from "64 is enough", "128 is absolutely enough" and "we've users with more 190 group SIDS).
NGROUPS_MAX as defined by different Unix versions are as follows (http://www.j3e.de/ngroups.html):
Linux Kernel >= 2.6.3 65536
Linux Kernel < 2>IBM AIX 5.2 64
IBM AIX 5.3 ... 6.1 128
OpenBSD, NetBSD, FreeBSD, Darwin (Mac OS X) 16 Sun Solaris 7, 8, 9, 10 16 (can vary from 0-32)
HP-UX 20
IRIX 16 (can vary from 0-32)
Plan 9 from Bell Labs 32
Minix 3 0 (Minix-vmd: 16)
QNX 6.4 8
Question 6
You are asked to troubleshoot networking issues on an unfamiliar system. Select the correct command to display what network devices are installed.
Correct Answer:C